
Streams will usually be braided if they have high bed loads and easily erodible banks. The water is diverted to the sides and erodes stream banks, widening the channel. The braiding generally results from a flood‐deposited midchannel bar that splits the flow. Braided streams typically have wide channels. A braided stream is one in which the water has lost its main channel and flows through a wandering network of rivulets around sandbars. The bottomset beds are the finest silt and clay particles that are carried out into the deeper water or slide down the delta front into the deeper water.īraided streams. These represent the gradual accumulations of sediment deposited over the forward slopes of the delta as it builds progressively outward into the receiving body of water. They overlie the sandy foreset beds that compose the main body of the delta, which dip downward from 5 to 25 degrees. Topset beds are nearly horizontal layers of sediment deposited by the distributaries as they flow away from the mouth and toward the delta front. Sediments on the delta's forward slopes are constantly shaped by water and wind action and redeposited by lake or ocean currents. Distributaries are dendritic, shifting channels that spread out across the delta from the main river channel and disperse the sediment load.


Sediment deposited at the mouth of a stream usually forms a thick, roughly wedge‐shaped accumulation called a delta, the widest part of which is farthest from the stream mouth. Large fans show graded patterns in which the coarsest‐grained materials are deposited at the canyon mouth and the finer‐grained materials spread outward in a fan shape.ĭeltas. Stream velocities fall quickly, and the fan is built by continual braided stream activity. Alluvial fans are similar to deltas and are large fanlike accumulations of sediment that form where streams emerge from rugged terrain onto a broad, flatter surface. The poorly drained and marshy areas behind the levees are called backswamps.Īlluvial fans. As the water spreads outward from the channel, it loses energy and carries less sediment. Higher ridges of sand and silt called natural levees are deposited near the edge of the channel. Floodplains are level strips of land on the sides of a channel that consist of fine‐grained silt and clay deposited during episodes of flooding. A subsequent flood event will erode bars, transport the sediments, and redeposit the material as a new bar farther downstream.įloodplains. Bars are ridges generally made up of gravel‐ or sand‐sized particles. Bars form in the middle of the channel or along the banks of a stream at points where the velocity decreases, resulting in the deposition of some of the sediment load. At the mouth of the stream, the sediments are usually deposited in alluvial fans or deltas, which represent a lower‐energy, more “permanent” depositional environment that is less susceptible to changes in the stream flow.īars. Sediments are deposited throughout the length of the stream as bars or floodplain deposits.
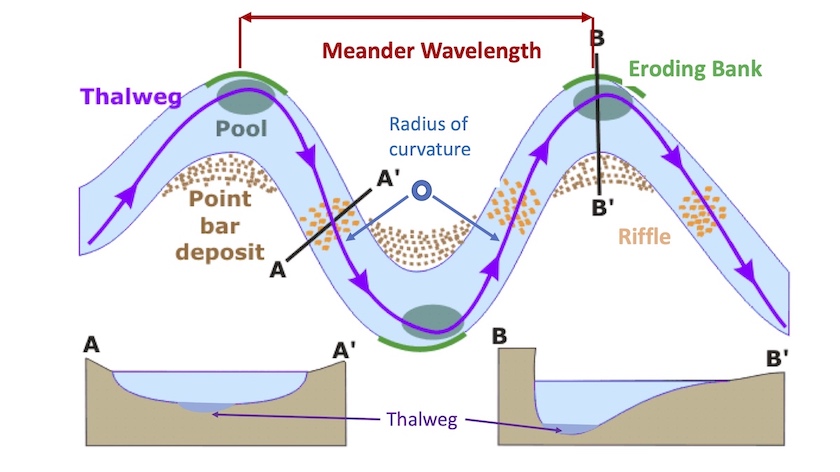
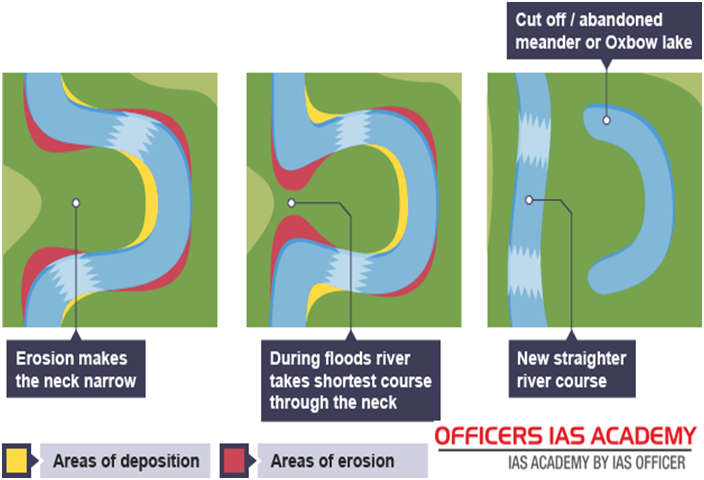
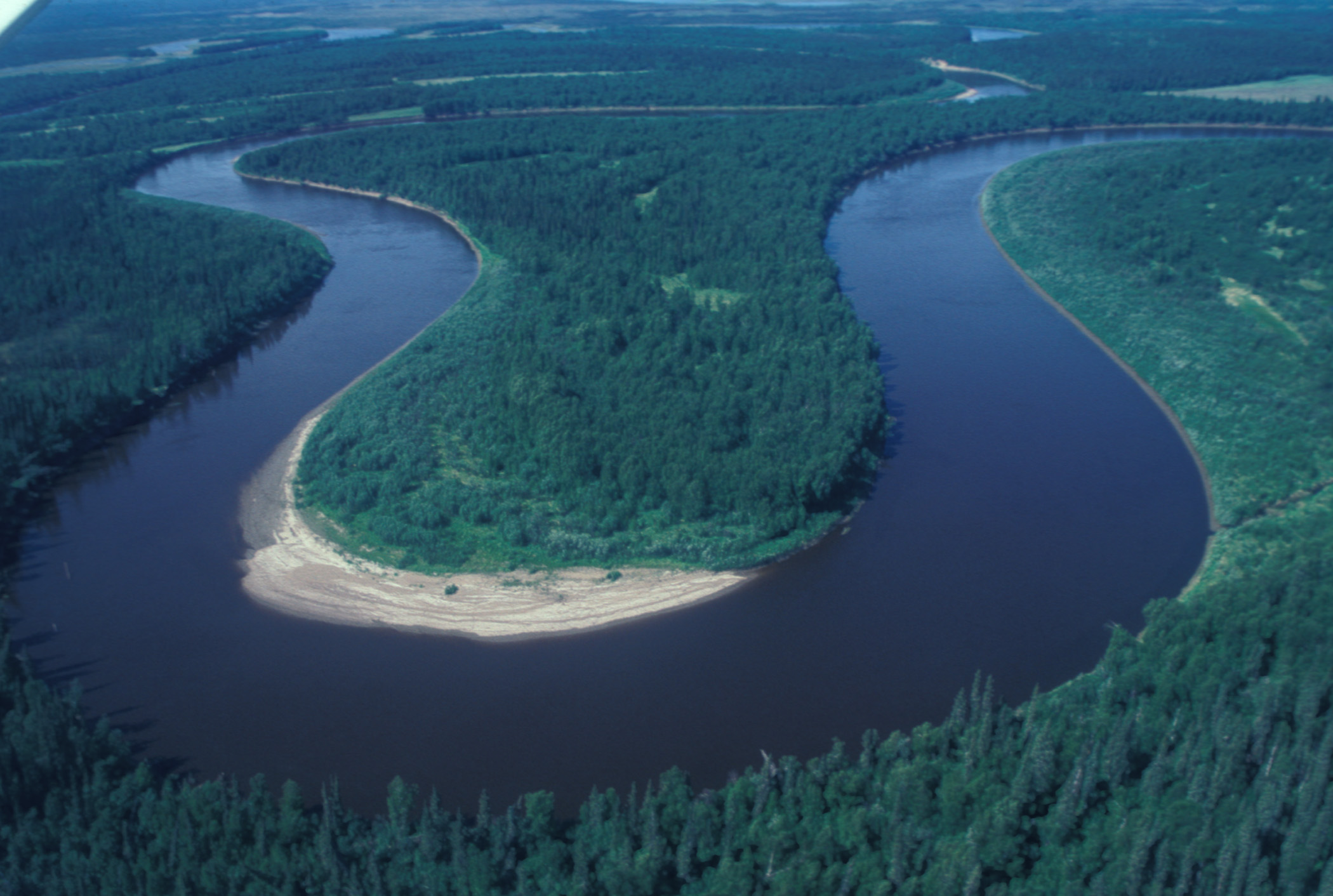
A stream's sediment load is typically deposited, eroded, and redeposited many times in a stream channel, especially during climatic variations such as flooding.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
